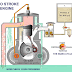
The engine motion is like this:
Two-stroke engines often provide high power-to-weight ratio, usually in a narrow range of rotational speeds called the "power band". Compared to 4-stroke engines, they have a greatly reduced number of moving parts, are more compact and significantly lighter.
The first commercial two-stroke engine involving in-cylinder compression is attributed to Scottish engineer Dugald Clerk, who in 1881 patented his design, his engine having a separate charging cylinder. The crankcase-scavenged engine, employing the area below the piston as a charging pump, is generally credited to Englishman Joseph Day.




0 comments:
Post a Comment